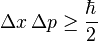19 November, 2011
Protect IP act and SOPA
18 November, 2011
The atomic structure [5]: Heisenberg uncertainty principle
The problem that was being posed now was if it could be possible to elaborate models that required the existence of precise orbits. To calculate the path of a certain dot, it necessary to know its position and speed at a certain moment.
In response to this problem Heisenberg proposed the uncertainty principle, according to which is not possible to measure accurately and contemporaneously the position and the speed of a certain particle
17 November, 2011
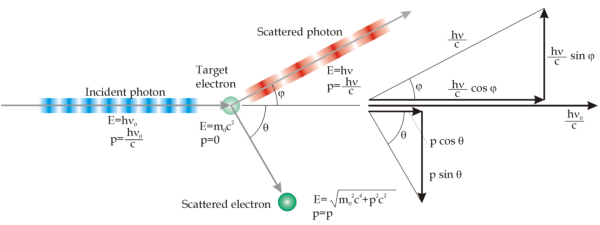
The atomic structure [4]: Wave-particle duality
Compton proposed that this phenomena could be explained as an interaction between particles: photons and electrons. Photons, interacting with graphite, are going to hit electrons, shifting part of they energy. The electron is therefore going to be emitted with a lower kinetic energy than the photon. It means that also the frequency will be lower, thus the wavelength will be higher, explaining the Compton scattering.
This new discovery, together with photoelectric effect, showed that light behaved ad a particle. De Broglie, was firmly convinced about unity in nature: if waves behaved like matter, also matter had to behave like waves. In 1924 he proposed that the motion of particles was related to the propagation of a certain wave, according to his hypothesis:
16 November, 2011
Is it worth saving pandas?
Those species are indeed very expensive to keep going, and most of the resources in this area are used toward them and a few others, while the best thing to do could be to preserve biodiversity hotspots. If habitat are not preserved, there's no point in talking about preserving biodiversity. So if we all the cash were not spent on those famous species but were used, for example, to buy rainforest, biodiversity might get greater benefits.
On the other hand megafauna like pandas and tigers appeal to people's emotional side, and attract a lot of attention, raising the possibility of higher money resources. It can lead to a media phenomena called single-species conservation. Those kind of advertising began in the seventies with Save the Tiger, Save the Panda, Save the Whale, and so on, but maybe this era has come to an end.
Nevertheless many species that could be "worth saving" live in a narrowly defined habitat. This mean that they don't need a big habitat to live in, and so the protected area would be restricted. In conservation terms is therefore better to try to protect the species that live at higher levels in the food web. Thus conservation will be extended to all the other species related to the protected one.
Furthermore protecting those species will require the conservation of larger habitats, than the one required by "lower" species. Megafauna could hence be used as media vehicle for the habitat conservation. There are things you pull out from the picture because people can relate to them. And it does make a difference.
15 November, 2011
The atomic structure[3]:the Bohr model
The problem related to the interpretation of those experimental results was solved by Niels Bohr in 1913, that modified Rutherford's model, according to Quantum Mechanics. The main ideas are:
- Electrons move around the nucleus in circular orbits (or elliptical, according to Sommerfeld) under the action of coulombian force;
- Electrons cannot orbit in every orbit, but only in the ones with a certain angular momentum;
- If electrons orbit in one of the allowed orbits, it doesn't radiate energy;
- The atom emits energy and radiations only when electrons pass from an higher energy stationary state, to a lower one.
The atomic structure[2]: the birth of quantum mechanics
- Black body radiation;
- Photoelettric effect;
- Compton scattering;
- Emission and adsorption spectrum of atoms.
13 November, 2011
The atomic structure [1]: the discovery of fundamental particles
- Everything is composed by invisible and indivisible particles, called atoms. This idea was present also in Greece over 2500 years earlier, because of Democrito.
- Atoms cannot be created and cannot be destructed;
- In a certain element, all the atoms are equal, sharing the same mass and chemical properties;
- Different elements are made by different atoms, with different mass and chemical properties;
- Different atoms can combine each other to form more complex particles
11 October, 2011
The photosynthetic slug

10 October, 2011
Warm-blooded reptiles?
A recent research by Holly Woodward, Jack Horner and colleagues at Montana State University (published online on PLoS ONE), proved that dinosaurs who lived at polar latitudes weren't physiologically different from other species, on the contrary of what claimed an earlier study, influenced by the lack of a good number of finds.
The endothermy hypothesis could also be supported by the presence of feathers on many dinosaur species, especially on theropods like dromaeosaurids. This group includes the notorious Velociraptor, and is probably a parallel evolutionary line to that of birds, with whom they could share a common ancestor. Structures like feathers or hair are typical in endothermic animals and are important in thermoregulation, as they act insulating the body and making it less influenced by changes in the environmental temperature.

Another study, published on "Science" and guided by researchers of Bonn University and the California Institute of technology, discovered what the internal temperature of sauropods was. This enormous herbivores had a body temperature similar to that of modern mammals, between 36 °C and 38 °C. They analyzed the teeth of these creatures, which contain carbonates made by different isotopes of carbon and oxygen. Since the temperature at which this compound is formed influences the percentage of 13C and 18O that bind together within the tooth, the higher the temperature was, the lower the frequency of this bond was. Analyzing the quantity of these isotopes, they determined the body temperature of these animals.

All these discoveries, but many others too, seem to prove that the most diversified and successful group of reptiles had a physiology similar to that of mammals, a fact that probably allowed them to colonize almost all the available environments.
09 October, 2011
Thermonuclear fusion: the confinement of plasma [3]
Inertial Confinement
In those reactors, plasma is obtained thanks to the use of high energy laser. Small spheres containing mixtures of Deuterium and Tritium are placed in a vacuum chamber.
Magnetic Confinement
Even though inertial confinement could soon reach a great energy efficiency, magnetic confinement seems to be closer to reach this aim. This reactor is based on the principle that plasma is composed by charged particles that are affected by Lorentz force.
According to this model, several types of reactors have been proposed and tested. The most efficient one resulted to be the "Stellarator", which uses further helicoidal spins to the ones of the toroid. This different geometry allows, for instance, to eliminate the assial current necessary in any other toroid to create the poloidal field (as we can see in the previous figure).
The main problem related to "Stellarator" is its extreme complexity. This model is indeed only a theoretic proposal and no one has been built yet. More simple reactors are based on the "Tokamak" geometry, which is the most widely used nowadays.
08 October, 2011
Thermonuclear fusion: deep inside the heart of stars [2]
According to this data, nuclear reaction should be impossible at those condition. However three other factors can combine to bring a certain probability of success for those reactions:
- Particles are characterized by a Maxwell speed distribution. It means that a certain amount of particles have a energy greater than the medium one, and a certain amount can reach the level required;
- According to quantum mechanics there's a little probability that a particle with low energy could exceed the coulombian barrier, by Quantum Tunnelling;
- Stars are made by a large amount of particles. Even though the medium level isn't enough to exceed the barrier, a great amount of particles could have enough energy.
The hidden twin of the Amazon River
There is an enormous amount of water, flowing very slowly for 6000 km, from the Andes to the Atlantic Ocean. With a width between 100 and 200 kilometers, the river "Hamza" is probably the world's biggest groundwater. Hamza and his team analyzed datas coming from several oil wells dug by the Petrobras company, between 1970 and 1980.

Thermonuclear Fusion: beyond particle physics [1]
If we consider two Hydrogen atoms, their nucleus consist of one proton. This means that they will be affected by a gaining repulsive electromagnetic force while getting closer. According to Coulomb law this force is:
The standard model of particle physics postulates the existence of two more forces: weak and strong nuclear forces. Those kind of forces do not affect every particle, and their radius of effect is very little: 10^-15 for the strong one and 10^-18 for the weak one. This explains why those forces are not familiar to us, and don't have any noticeable effect on macroscopic world.
Particles are divided in several categories:
- Leptons: those particles are fundamental. It means that they aren't made up by other particles and aren't affected by strong nuclear force, but only by the weak one. Are divided in three other categories: electron, muon, tau. Everyone of them has a corresponding neutrino.
- Hadrons: those are massive particles, affected by all the 4 fundamental forces. Nowadays are known more than a hundred of those particles, even though proton is the only stable one. Are made up by quarks, and are divided in two further categories, Baryons an Mesons
"Two fermions cannot occupy simultaneously the same quantum state"
- Fermions: particles with one half spin, obeying to Pauli principle;
- Bosons: particles with integer spin, that do not obey to Pauli principle. Are also known as quantum mediator.
Strong nuclear force allows the creation of atomic nucleus. It is deeply related to binding energy, which is defined as:
"The energy required to break the bond between protons and neutrons inside the nucleus."This energy is different for every nucleon, because depends on mass number. It increases with mass number for elements lighter than iron, and then decreases. The fusion of two lighter atoms will then lead to the formation of a heavier and more energetic atom, allowing the liberation of a certain amount of energy.
The mass of the resulting atom will be in fact lower than the sum of the two lighter ones. According to Einstein's special relativity this mass is transformed in energy.
07 October, 2011
Possible solutions to energy crisis
- Nuclear Power;
- Wind;
- Solar thermal;
- Solar photovoltaic;
- Geothermal;
- Hydroelectric.
06 October, 2011
From raw materials to nanotechnology




From “wafers” to transistors…





Several metal layers compose “think wires” between transistors, which are extremely important for CPU structure and functions.
 Now the CPU building is complete, but the product has to be tested: every transistor and circuit is controlled in order to check the right functioning of the whole system.
Now the CPU building is complete, but the product has to be tested: every transistor and circuit is controlled in order to check the right functioning of the whole system.